ESPOT (ElectroStatic POTential maps), an extension of SAED6 and QSAED6. ESPOT is designed to calculate projected atomic potential maps from diffraction data generated by SAED6. These maps can be correlated with high-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) images and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) structural images taken under Scherzer conditions. By combining the diffraction data retrieved from experimental patterns using QSAED6, users can obtain projected atomic potential difference maps to analyze and improve structural models. This method is analogous to the approach used by X-ray crystallographers to calculate electron density maps and difference electron density maps. Due to the geometry of electron diffraction, it is straightforward to obtain two-dimensional electron diffraction patterns. Consequently, ESPOT was developed to calculate projected atomic potential maps and projected atomic potential difference maps. ESPOT features two main interfaces: one for displaying the calculated diffraction pattern or comparing calculated and experimental diffraction patterns, and another for calculating and displaying the projected atomic potential map. It offers three types of projected atomic potential difference maps. More details of these features are described in the user manual. |
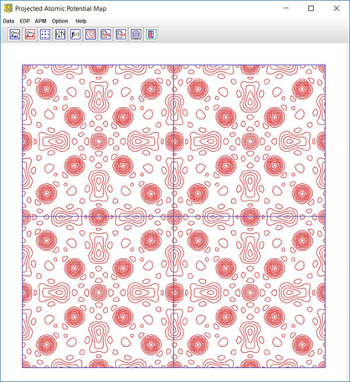
GUI of ESPOT with a projected atomic potential map of an example, in which the input data was prepared from SAED6.